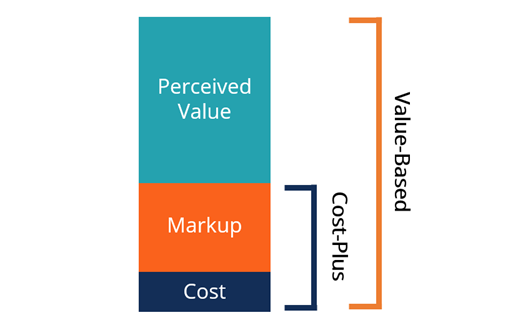
Cost Plus pricing strategy is the most rudimentary of all the pricing strategies. It is probably the first one that we intuitively learn even before formally learning about pricing. And we do have numerous cost plus pricing strategy examples as well.
Our minds are hardwired to a few things. How much money it took us to buy something? How much money we want to make from it? Also, how much should we sell it for? Anything that fits this thought process in your head would actually serve as a good cost plus pricing strategy example.
Also Read: How to Price Your Product – The Fundamentals
Importance of Pricing for Marketers
Now, as a marketer, pricing is one of those critical factors in marketing. You will not only have to understand it but some expertise in it to do well. For that you need to understand the value of pricing for you as a business.
Most of the time we interact with pricing predominantly when discussing the marketing mix but forget about the central role that pricing plays in the profitability of a business
Business is basically- a venture that you and I would get into for making profits.
Interestingly, there are numerous pricing strategies that you are already acquainted with. Where did you learn them ? Probably, in your Bachelors or your MBA course.
Let us take a look at some factors that are employed by marketers. They primarily use it to arrive at the final prices of products are:
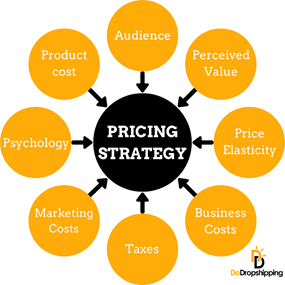
Source - DoDropshipping pricing strategy
If you remember correctly, we tackled the topic of price-quality based positioning sometime back and went into some length on how price affects the perceived quality of a product and profitability.
In this article, we will explore the most rudimentary of all pricing strategies – the cost plus pricing strategy. Further, I will take you through some cost plus pricing strategy examples.
First, let us look at some of the examples of industries or products which have used cost plus pricing.
Meaning of Cost Plus Pricing Strategy?
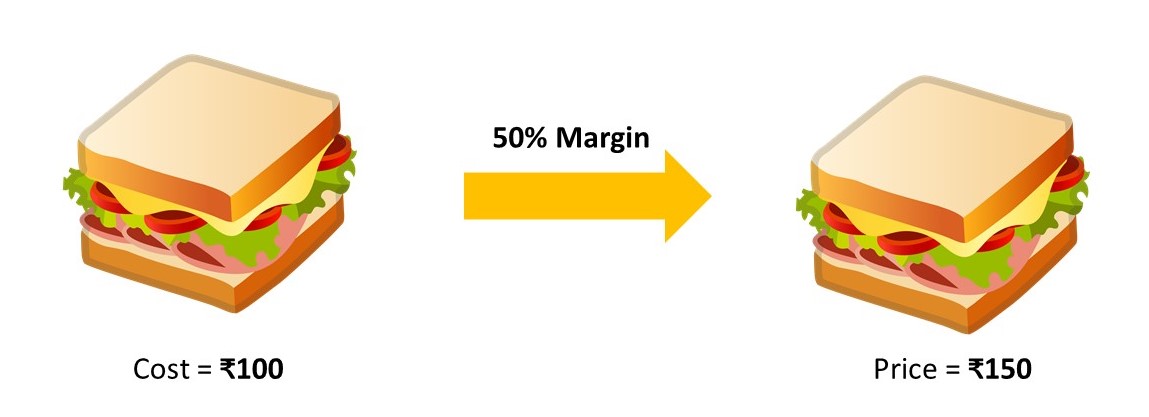
Let us start with a very basic cost plus pricing strategy example. Suppose that the cost of a sandwich that you want to sell is ₹100 to you. This price includes all the costs that have been involved in making this sandwich, everything that you can think of.
So, even if you had spent in printing pamphlets to distribute it in your locality, even those marketing costs are included.
How you would attribute the price of marketing per sandwich ? We will discuss that later.
As the seller, you can decide to add a percentage on top of this ₹100 cost. Say, for example 50% of the total costs. The added potion of ₹50 will then be your profit.
Hence, you followed a cost plus pricing strategy by arriving at a list price of ₹150 for the sandwich.
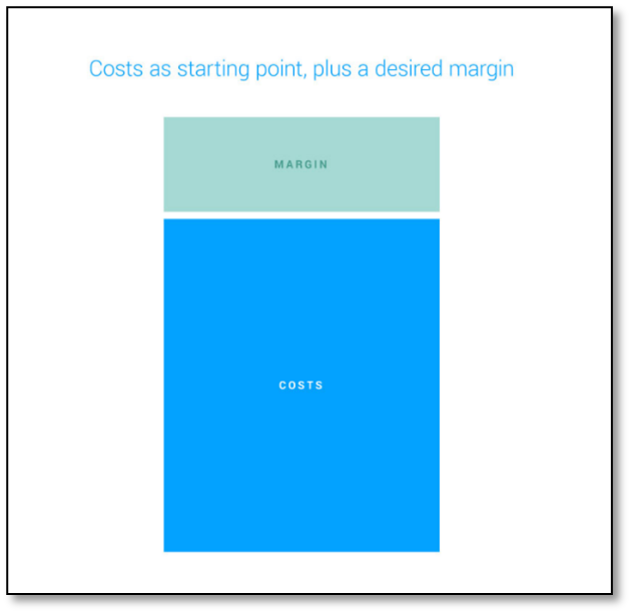
So, what do we do in the cost plus method?
We multiply the total input cost by the markup percentage and get the final price.
Source - Omniaretail blog
One thing to note here is that the markup percentage is completely at the disposal of the seller. There is sufficient freedom to vary this percentage in the Cost plus method.
Basic Intuition behind Cost Plus Pricing Strategy
The notion behind the cost plus pricing approach is simple; basically, you will calculate the entirety of costs involved in the manufacturing of the product. You will then decide on a markup percentage of these costs.
And then you add it to the cost to determine the selling price.
It is quite an interesting approach to make sure that you earn a pre-decided profit. In my article on Disadvantages of Cost Plus Pricing Strategy, however, we will see that it may not always be as straightforward. And that your calculation of the profits that you will get from this approach may not always be correct.
You must be wondering what are the advantages of cost plus pricing strategy. Lets have a look at why businesses go for cost plus method.
Advantages of Cost Plus Pricing Method
After weighing in all the factors, here are some of the advantages of Cost plus method:
1. Ease of Understanding: Ask anybody who understands simple business and wants to earn profit, to come up with the price of a product. The first strategy that they will unknowingly apply is Cost Plus pricing method. That’s how we look at business. We factor in the input cost, add our desired profit and come up with the final price. It’s that simple!
2. Freedom with Markup percentage: It is completely dependent on the seller to determine the profits that are to be earned. This ensures that there is freedom to vary this percentage for different commodities.
3. Easily to Justify: This strategy does not require any fancy terms and games to be played with the consumer. You can very simply explain how you did price the products. If a price increase is causing an upheaval, what can you do ?
Notify the consumers about the increase in input cost and justify the increase.
Cost Plus Pricing Strategy Examples and Where Does it Work ?
Let say that Reliance Industries Limited(RIL) hires you in their sales and marketing department.
Suppose that Reliance Industry Limited(RIL) has recently been the beneficiary of a 10-year government contract. .
In order to achieve its goals, Reliance Industries sets up a small power plant. It plans to operate and maintain it over the ten years period of the contract.
RIL is entitled to monthly reimbursements for cost incurred for each unit of electricity consumed. Along with that, it gets a 20% profit on the cost of supplying the electricity.
Accordingly, RIL incurs labor costs of $20,000 per month for employee costs. Add to it an additional $20,000 per month for costs of diesel consumed monthly. Also, account the $15,000 monthly depreciation of plant and $10,000 for the management’s fee.
Using the cost plus strategy, Reliance Industries will charge costs of $65,000, and add 20% of the cost, as their profit. The invoiced amount for the first month will, therefore, be $78,000.
All figures used in the above cost strategy example quoted are figurative. Here, the idea is to explain you to the crux of this pricing strategy.
Ideally, the cost-based pricing can be very easily applied for predetermined percentage as profits.
Despite its popularity, this approach finds praise and criticism alike, particularly in pricing literature.
Is Cost Plus a Good Way to Price?
There are reasons as to why cost plus pricing strategy is not the first choice. Let’s just observe a easier example below. It helps to understand why it could turn out to be a bad idea.
Later on, I will build upon from this very thought that what could be a better a pricing strategy i.e. the Value-Based Pricing strategy.
Say you have manufactured a product which has cost you ₹300. Imagine that you desire a 50% margin, thus you wil price this product at ₹450.
Now assume that the market is willing to pay up to ₹650 for your product.
This means that with the cost plus pricing approach you will lose out on your optimal profit. It could have been much more than just ₹150.
Now let us assume that the market is instead only willing to pay ₹375 for the same product.
What happens now?
You will be tempted to leave the money on the table and not sell your product. Why ? Because your margin is not met in this case.
In both of these cost plus pricing strategy examples, we see that pricing is based on a random number or figure, as opposed to being supported by the amount of money that the consumer is willing to buy.
Which means the cost plus pricing doesn’t capture the essence of the value that the product is to the customer.
Disadvantages of Cost Plus Pricing Strategy
Though this is covered at length in one of my articles- Disadvantages of Cost plus Pricing Strategy, I will give you some understanding here about why Cost Plus pricing method is not a good idea.
Some of the disadvantages of cost plus method is that it does not account for anything about the competition. This is evident from the cost plus pricing strategy examples we have considered. Your price may be set too high or too low because you have solely decided it based on your desired profits.
Another major disadvantage of cost plus method is that it does not take customer expectations into consideration. There is no incentive for adjusting the prices according to changing market scenario. This may lead to anomaly between your prices and the perceived value of your product or service.
Conclusion
As you have observed, the cost plus pricing method is one of the most basic methods of pricing. It is no surprise that it is also one of the more popular methods.
- You just need to add your desired profits to the input cost. And then, you arrive at the selling cost.
- Cost plus pricing method is generally in use when physical goods are involved specially in manufacturing companies.
- With services , it become very difficult to follow the cost plus method.
- However, it does have some major merits and demerits that you may have to consider before you select this approach.
On the next article, we will go into depth on the efficacy of this costing approach. We will analyse why it may be or may not be the best fit for your company.